- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
Types of Hair loss: Signs, Causes and the Role of Finpecia

The Role of Finpecia (Finasteride)
Finpecia, or finasteride, is a medication primarily prescribed for male pattern baldness.
Its role in managing this type of hair loss includes:
Slowing Hair Loss: Finpecia works by inhibiting the enzyme that converts testosterone into DHT, which is associated with hair loss. By reducing DHT levels, it can slow the progression of male pattern baldness.
Promoting Hair Regrowth: In some cases, Finpecia can stimulate hair regrowth in areas where hair follicles have not completely miniaturized.
Maintenance Treatment: To maintain its benefits, Finpecia is often taken continuously, as discontinuing its use can lead to a return of hair loss.
Prescription Medication: It is available by prescription only and should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Side Effects: Users should be aware of potential side effects, including sexual dysfunction and mood changes, and discuss these with their healthcare provider.
It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause of hair loss and to discuss suitable treatment options, including medications like Finpecia. Treatment decisions should be tailored to individual needs and circumstances. Women of childbearing age should exercise caution when using finasteride, as it can cause birth defects in a developing male fetus if taken during pregnancy.
Types of Hair Loss:
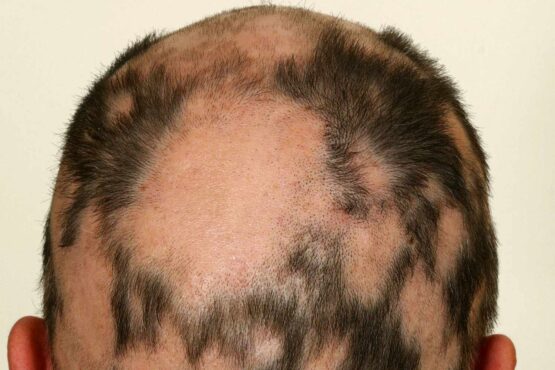
Androgenetic Alopecia (Male and Female Pattern Baldness)
A common hereditary form of hair loss characterized by a progressive thinning of hair in a specific pattern, often seen in both men and women.
Signs: gradual hair thinning; receding hairline in men; widening part in women.
Causes: genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances (especially dihydrotestosterone, or DHT), and aging.
Role of Finpecia: Finpecia, containing the active ingredient finasteride, is often prescribed to manage androgenetic alopecia, primarily in men. It works by reducing DHT levels, which helps slow hair loss and may stimulate hair regrowth.
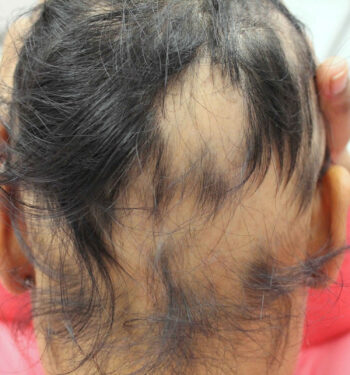
Alopecia Areata
An autoimmune condition that results in the sudden loss of hair, often in small, round patches on the scalp or other parts of the body.
Signs: Sudden, round, or oval patches of hair loss on the scalp or other areas.
Causes: autoimmune disorder, where the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles.
Role of Finpecia: Finpecia is not typically used for alopecia areata, as the condition has an autoimmune origin and requires different treatments, such as corticosteroids or immunotherapy.
Anagen Effluvium
Is a type of hair loss characterized by the sudden and widespread shedding of hair, typically caused by factors such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or exposure to toxins, disrupting the active growth phase of hair follicles.
Signs: sudden hair loss during the anagen (growth) phase, often due to chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Causes: Exposure to toxins or drugs that affect rapidly dividing cells.
Role of Finpecia: Finpecia is not used for anagen effluvium since it doesn’t address the underlying cause.
To find out more you can watch our YouTube videos: